JvaScript
Expressions and operators
- Operators: JavaScript has the following types of operators. This section describes the operators and contains information about operator precedence.Assignment operators, Comparison operators, Arithmetic operators, Bitwise operators, Logical operators, String operators, Conditional (ternary) operator, Comma operator, Unary operators and Relational operators.

- Expressions: An expression is any valid unit of code that resolves to a value.
Every syntactically valid expression resolves to some value but conceptually, there are two types of expressions: with side effects (for example: those that assign value to a variable) and those that in some sense evaluate and therefore resolve to a value.
The expression x = 7 is an example of the first type. This expression uses the = operator to assign the value seven to the variable x. The expression itself evaluates to seven.
The code 3 + 4 is an example of the second expression type. This expression uses the + operator to add three and four together without assigning the result, seven, to a variable.
- JavaScript has the following expression categories:
- Arithmetic: evaluates to a number, for example 3.14159. (Generally uses arithmetic operators.)
- String: evaluates to a character string, for example, “Fred” or “234”. (Generally uses string operators.)
- Logical: evaluates to true or false. (Often involves logical operators.)
- Primary expressions: Basic keywords and general expressions in JavaScript.
- Left-hand-side expressions: Left values are the destination of an assignment.

Loops and iteration
- Loops offer a quick and easy way to do something repeatedly. This chapter of the JavaScript Guide introduces the different iteration statements available to JavaScript. There are many different kinds of loops, but they all essentially do the same thing: they repeat an action some number of times. (Note that it’s possible that number could be zero!).
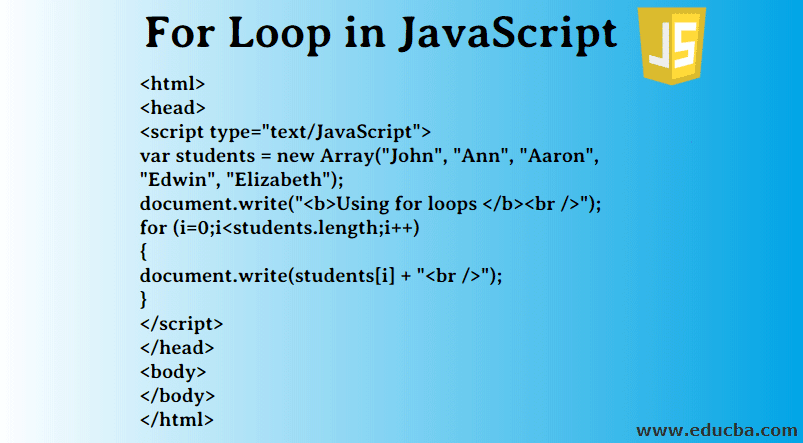
- The statements for loops provided in JavaScript are:
- for statement.
- while statement.
- labeled statement.
- do…while statement.
- break statement.
- continue statement.
For Statement:
- A for loop repeats until a specified condition evaluates to false. The JavaScript for loop is similar to the Java and C for loop. When a for loop executes, the following occurs:
- The initializing expression initialExpression, if any, is executed. This expression usually initializes one or more loop counters, but the syntax allows an expression of any degree of complexity. This expression can also declare variables.
- The conditionExpression expression is evaluated. If the value of conditionExpression is true, the loop statements execute. If the value of condition is false, the for loop terminates. (If the condition expression is omitted entirely, the condition is assumed to be true.)
- The statement executes. To execute multiple statements, use a block statement ({ … }) to group those statements.
- If present, the update expression incrementExpression is executed.
- Control returns to Step 2.
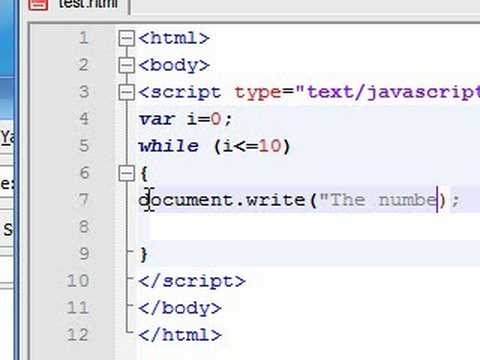
While statement:
- A while statement executes its statements as long as a specified condition evaluates to true, If the *condition *becomes false, statement within the loop stops executing and control passes to the statement following the loop. The condition test occurs before statement in the loop is executed. If the condition returns true, statement is executed and the condition is tested again. If the condition returns false, execution stops, and control is passed to the statement following while.To execute multiple statements, use a block statement ({ … }) to group those statements.
- For more information please visit this site Loops and Iteration



