Forms and JS Events
forms
The best known form on the web is probably the search box that sits right in the middle of Google’s homepage. for more information please visit CSS wireFrame
how Forms Work
You voted for Herbie Hancock.A user fills in a form and then presses a button to submit the information to the server.
<form action="http://www.example.com/subscribe.php"method="get">
<p>This is where the form controls will appear.</p>
</form>
Checkbox

<form action="http://www.example.com/profile.php"> <p>Please select your favorite music service(s): <br />
<input type="checkbox" name="service"
value="itunes" checked="checked" /> iTunes
<input type="checkbox" name="service"
value="lastfm" /> Last.fm
<input type="checkbox" name="service"
value="spotify" /> Spotify
</p>
</form>
form controlls
There are several types of form controls that you can use to collect information from visitors to your site.
Email & url Input
<input>
HTML5 has also introduced inputs that allow visitors to enter email addresses and URLs. Browsers that do not support these input types will just treat them as text boxes.
summary
- Whenever you want to collect information from
- visitors you will need a form, which lives inside a < form> element.
- Information from a form is sent in name/value pairs. Each form control is given a name, and the text the user types in or the values of the options they select are sent to the server.
Lists, Tables and Forms
<h1>The Complete Poems</h1>
<h2>Emily Dickinson</h2>
<ol> <li>Life</li>
<li>Nature</li>
<li>Love</li>
<li>Time and Eternity</li>
<li>The Single Hound</li>
</ol>
-
outside: The marker sits to the left of the block of text. (This is the default behaviour if this property is not used.)
-
inside: The marker sits inside the box of text (which is indented).In the example shown, the width of the list has been limited to 150 pixels. This ensures that the text wraps onto a new line so you can see how the value of inside sits the bullet inside the first line of text.
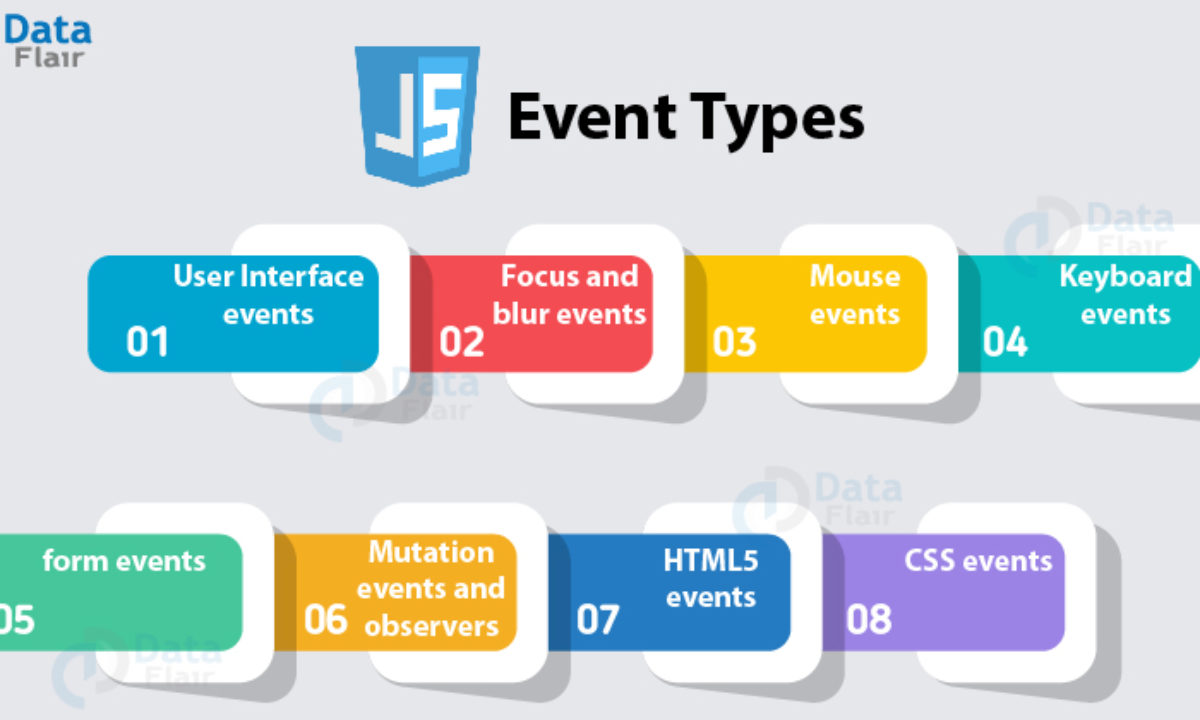
different event types
UI events Occur when a user interacts with the browser’s user interface rather than the web page.
terminology
-
EVENTS FIRE OR ARE RAISED When an event has occurred, it is often described as having fired or been raised. In the diagram on the right, if the user is tapping on a link, a click event would fire in the browser.
-
EVENTS TRIGGER SCRIPTS Events are said to trigger a function or script. When the click event fires on the element in this diagram, it could trigger a script that enlarges the selected item.
how events trigger javascript code:
- Select t he element node(s) you want the script to respond to
- Indicate which event on the selected node(s) will trigger the response.
- State the code you want to run when the event occurs.
three ways to bind an event to an element:
- HTML EVENT HANDLERS
- TRADITIONAL DOM EVENT HANDLERS
- DOM LEVEL 2 EVENT LISTENERS
HTML EVENT HANDLER ATTRIBUTES (DO NOT USE)
function checkUsername() {
var elMsg = document .getElementByi d('feedback') ;
var elUsername = document .getEl ementByld('username ');
if (elUsername .value .length < 5) {
elMsg.textContent ' Username must be 5 characters or more';
else {
elMsg.textContent = '';
USING PARAMETERS WITH EVENT HANDLERS and LISTENERS:
Because you cannot have parentheses after the function names in event handlers or listeners, passing arguments requires a workaround.
EVENT DELEGATION
Creating event listeners for a lot of elements can slow down a page, but event flow allows you to listen for an event on a parent element.
CHANGING DEFAULT BEHAVIOR
- preventDefau1t ()
- stopPropagation()
USER INTERFACE EVENTS
User interface CUI) events occur as a result of interaction with the browser window rather than the HTML page contained within it, e.g., a page having loaded or the browser window being resized.
summary
-
When an event occurs on an element, it can trigger a JavaScript function. When this function then changes the web page in some way, it feels interactive because it has responded to the user.
-
You can use event delegation to monitor for events that happen on all of the children of an element.
-
The most commonly used events are W3C DOM events, although there are others in the HTMLS specification as well as browser-specific events.
