Images
- Controlling the size and alignment of your images using CSS keeps rules that affect the presentation of your page in the CSS and out of the HTML markup.
- You can also achieve several interesting effects using background images. In this chapter you will learn how to:
- Specify the size and alignment of an image using.
- Add background images to boxes.
- Create image rollovers in CSS.
- controllIng sIzes of Images In css:
img.large { width: 500px; height: 500px;} img.medium { width: 250px; height: 250px;}img.small { width: 100px; height: 100px;} -
You can control the size of an image using the width and height properties in CSS, just like you can for any other box. Specifying image sizes helps pages to load more smoothly because the HTML and CSS code will often load before the images, and telling the browser how much space to leave for an image allows it to render the rest of the page without waiting for the image to download.

- aligning Images Using CSS:
img.align-left { float: left; margin-right: 10px;}img.align-right { float: right; margin-left: 10px;}img.medium { width: 250px; height: 250px;}centerIng Images using CSS:
img.align-center { display: block; margin: 0px auto;} img.medium { width: 250px; height: 250px;} - Once it has been made into a block-level element, there are two common ways in which you can horizontally center an image:
- On the containing element, you can use the text-alignproperty with a value of center.
- On the image itself, you can use the use the margin property and set the values of the left and right margins to auto.
- background-image:
body { background-image: url("images/pattern.gif");}p { background-image: url("images/pattern.gif");} - repeatIng Images:
- repeat: The background image is repeated both horizontally and vertically (the default way it is shown if the background-repeat property isn’t used).
- repeat-x: The image is repeated horizontally only (as shown in the first example on the left).
- repeat-y: The image is repeated vertically only. no-repeat: The image is only shown once.The background-attachment property specifies whether a background image should stay in one position or move as the user scrolls up and down the page. It can have one of two values:
- fixed: The background image stays in the same position on the page.
- scroll: The background image moves up and down as the user scrolls up and down the page.
- background-position:
body { background-image: url("images/tulip.gif"); background-repeat: no-repeat; background-position: center top;}

- Image rollovers & sprits:
a.button { height: 36px; background-image: url("images/button-sprite.jpg"); text-indent: -9999px; display: inline-block;}a#add-to-basket { width: 174px; background-position: 0px 0px;}a#framing-options { width: 210px; background-position: -175px 0px;}a#add-to-basket:hover { background-position: 0px -40px;}a#framing-options:hover { background-position: -175px -40px;}a#add-to-basket:active { background-position: 0px -80px;}a#framing-options:active { background-position: -175px -80px;} - css3: gradients:

- Summary :
- You can specify the dimensions of images using CSS. XThis is very helpful when you use the same sized images on several pages of your site.
- Images can be aligned both horizontally and vertically Xusing CSS.
- You can use a background image behind the box Xcreated by any element on a page.
- Background images can appear just once or be Xrepeated across the background of the box.
- You can create image rollover effects by moving the Xbackground position of an image.
- To reduce the number of images your browser has to Xload, you can create image sprites.
Practical information
-
To wrap up the book we are going to look at some practical information that will help you launch a successful site.
- search engine optimization (seo): SEO is a huge topic and several books have been written on the subject. The following pages will help you understand the key concepts so you can improve your website’s visibility on search engines.
- on-Page seo: In every page of your website there are seven key places where keywords (the words people might search on to find your site) can appear in order to improve its findability.
- analytics: learning aBout your Visitors:

-
As soon as people start coming to your site, you can start analyzing how they found it, what they were looking at and at what point they are leaving. One of the best tools for doing this is a free service offered by Google called Google Analytics.
- hoW many PeoPle are coming to your site?
- The overview page gives you a snapshot of the key information you are likely to want to know. In particular, it tells you how many people are coming to your site.
- Visits: This is the number of times people have come to your site. If someone is inactive on your site for 30 minutes and then looks at another page on your site, it will be counted as a new visit.
- unique Visits: This is the total number of people who have visited your site over the specified period. The number of unique visits will be lower than the number of visits if people have been returning to your site more than once in the defined period.
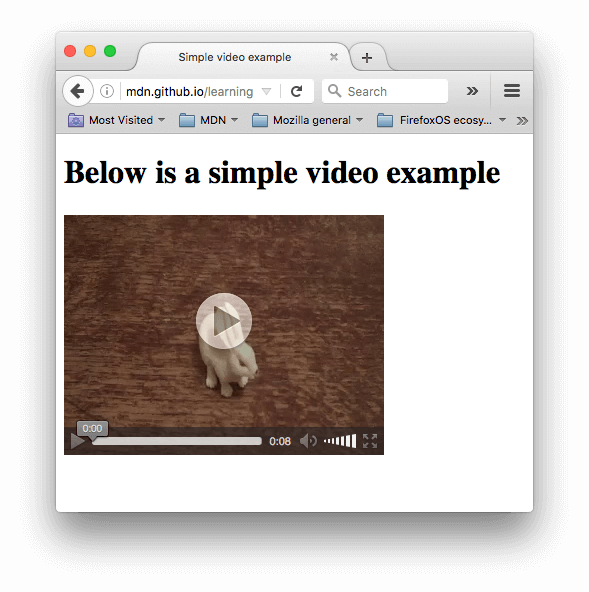
Video and Audio APIs
HTML5 comes with elements for embedding rich media in documents — <video> and <audio> — which in turn come with their own APIs for controlling playback, seeking, etc. This article shows you how to do common tasks such as creating custom playback controls.
<video controls>
<source src="rabbit320.mp4" type="video/mp4">
<source src="rabbit320.webm" type="video/webm">
<p>Your browser doesn't support HTML5 video. Here is a <a href="rabbit320.mp4">link to the video</a> instead.</p>
</video>
summary
- To put your site on the web, you will need to obtain a domain name and web hosting.
- FTP programs allow you to transfer files from your local computer to your web server.
- Many companies provide platforms for blogging, email newsletters, e-commerce and other popular website tools (to save you writing them from scratch). please visit Practical information.