Putting it all together
React is, in our opinion, the premier way to build big, fast Web apps with JavaScript. It has scaled very well for us at Facebook and Instagram.
Start With A Mock
Imagine that we already have a JSON API and a mock from our designer. The mock looks like this:
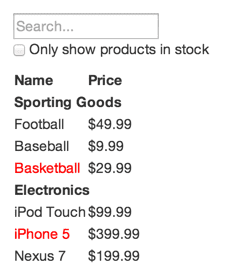
Our JSON API returns some data that looks like this:
[
{category: "Sporting Goods", price: "$49.99", stocked: true, name: "Football"},
{category: "Sporting Goods", price: "$9.99", stocked: true, name: "Baseball"},
{category: "Sporting Goods", price: "$29.99", stocked: false, name: "Basketball"},
{category: "Electronics", price: "$99.99", stocked: true, name: "iPod Touch"},
{category: "Electronics", price: "$399.99", stocked: false, name: "iPhone 5"},
{category: "Electronics", price: "$199.99", stocked: true, name: "Nexus 7"}
];
questions
- What is the single responsibility principle and how does it apply to components?
The single-responsibility concept is a computer programming concept that asserts that each module, class, or function in a computer program should be responsible for just one aspect of its functioning and should encapsulate that aspect so using the same techniques for deciding if you should create a new function or object. One such technique is the single responsibility principle, that is, a component should ideally only do one thing. If it ends up growing, it should be decomposed into smaller subcomponents.
- What does it mean to build a ‘static’ version of your application?
To build a static version of your app that renders your data model, you’ll want to build components that reuse other components and pass data using props. props are a way of passing data from parent to child. If you’re familiar with the concept of state, don’t use state at all to build this static version
- What are the three questions you can ask to determine if something is state?
-
Is it passed in from a parent via props? If so, it probably isn’t state.
-
Does it remain unchanged over time? If so, it probably isn’t state.
-
Can you compute it based on any other state or props in your component? If so, it isn’t state.
- How can you identify where state needs to live?
so we’ve identified what the minimal set of app state is. Next, we need to identify which component mutates, or owns, this state.
Remember: React is all about one-way data flow down the component hierarchy. It may not be immediately clear which component should own what state
Higher-Order Functions

A large program is a costly program, and not just because of the time it takes to build. Size almost always involves complexity, and complexity confuses programmers. Confused programmers, in turn, introduce mistakes (bugs) into programs.
```
let total = 0, count = 1;
while (count <= 10) {
total += count;
count += 1;
}
console.log(total);
questions
- What is a “higher-order function”?
Functions that operate on other functions, either by taking them as arguments or by returning them, are called higher-order functions. Since we have already seen that functions are regular values, there is nothing particularly remarkable about the fact that such functions exist.
- Explore the greaterThan function as defined in the reading. In your own words, what is line 2 of this function doing? this returning another function
arrow function. it will return m arrow m greater than n and it is arrow function
- Explain how either map or reduce operates, with regards to higher-order functions.
The map method transforms an array by applying a function to all of its elements and building a new array from the returned values. The new array will have the same length as the input array, but its content will have been mapped to a new form by the function.
Summary
Being able to pass function values to other functions is a deeply useful aspect of JavaScript. It allows us to write functions that model computations with “gaps” in them. The code that calls these functions can fill in the gaps by providing function values.
click here to read more Higher-Order Functions: